Shop by Servers
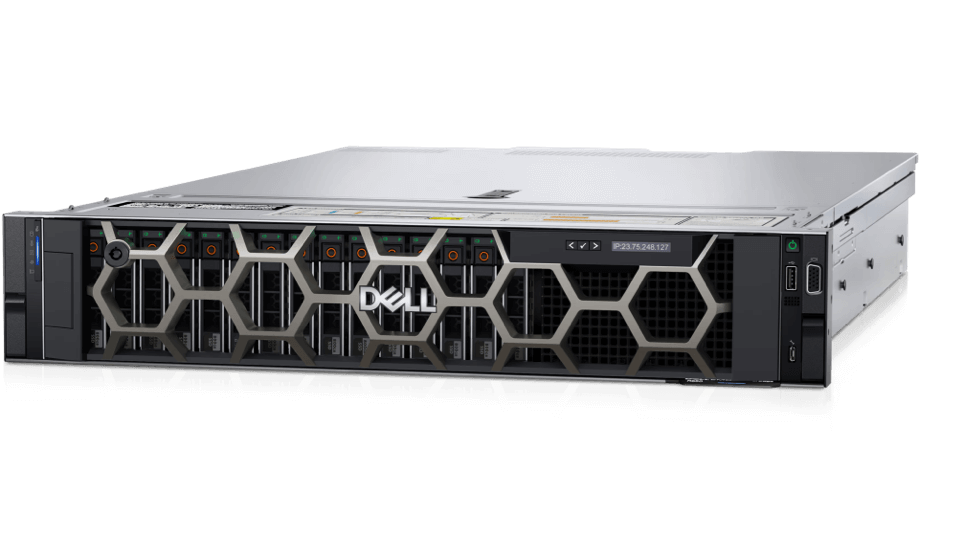
General Purpose Server
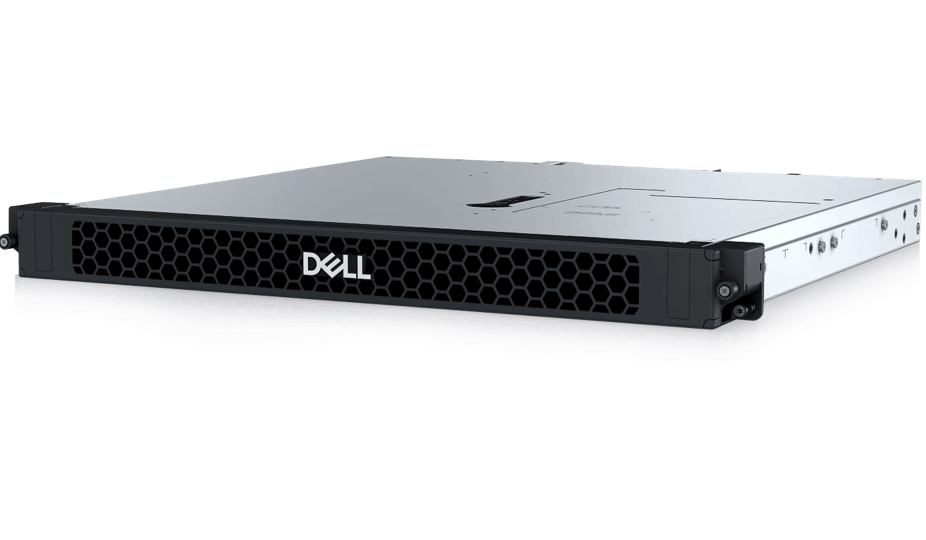
Edge Server
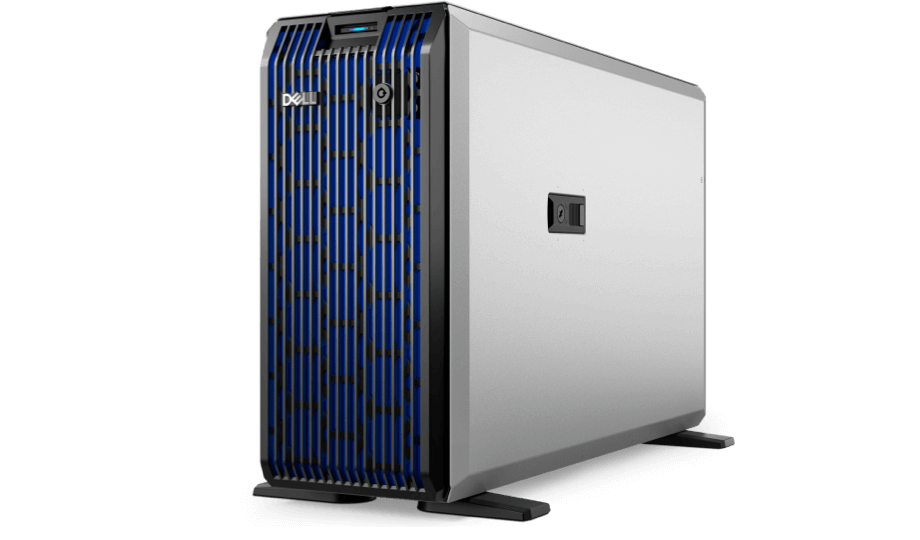
Workstation
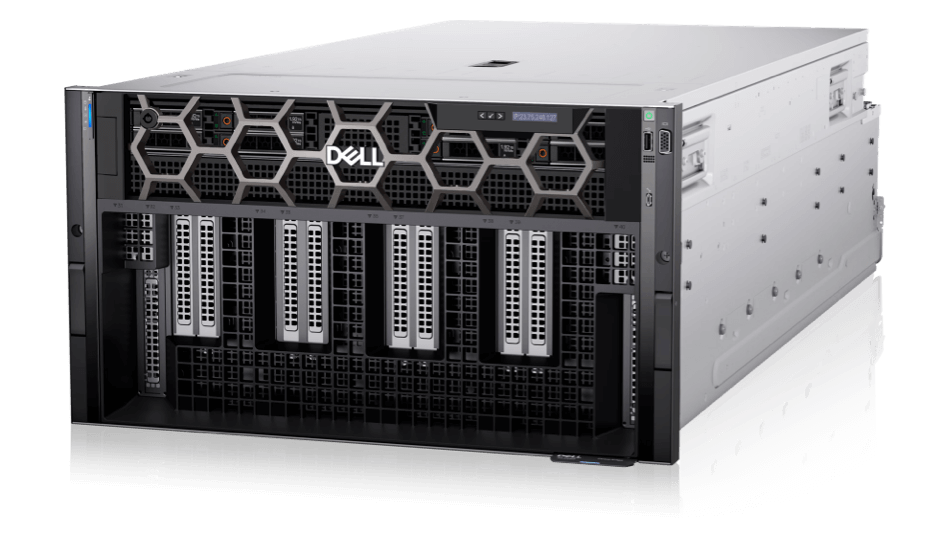
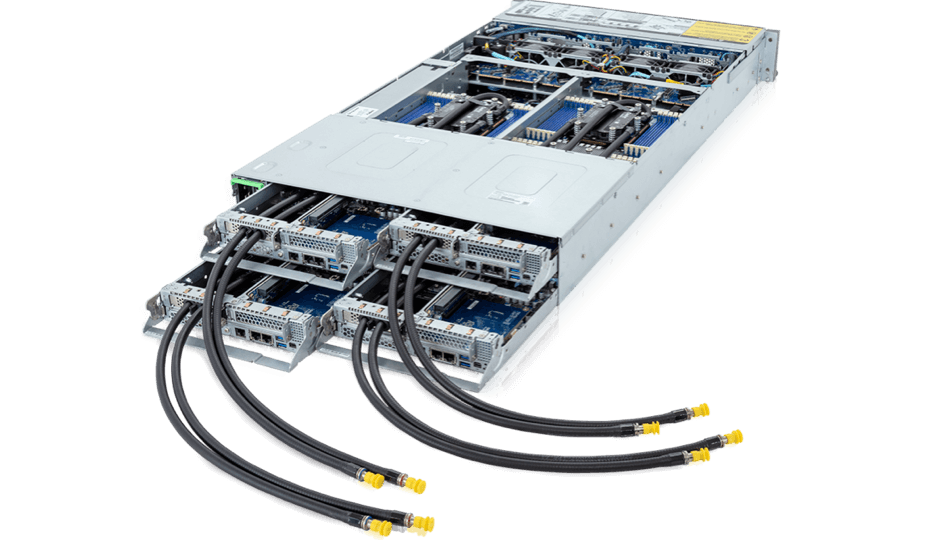
AI/ML/HPC Server
High Density Server
Storage Server
The commonest traditional mode combined with versatile performance
Scalable infrastructure with high density 1, 2 or 4 socket of CPU processors Availible for both Intel and AMD processors Ideal for common business applications,virtualization and cloud-native workloads.Designed for continuous operation in extreme environments
Compact, ruggedized, customized depth rugged OEM-ready server with reverse mounting capabilities.Built for telecom, retail, marine and government applications.Compact and quiet construction designed for small businesses and remote offices
Availible 1 or 2 socket CPU options to meet different needs like 3D rendering, CAD, and video editing, providing robust computing power and advanced graphics capabilities.Specialized servers equipped with AI-optimized CPUs or GPUs, and designed for extensive AI model training and inference tasks.
Rapidly develop, train and deploy large machine learning models with high-performance application servers designed for HPC supercomputing and the largest data sets for AI.Compact servers designed for maximize performance in limited space.
They offer high compute power in a small footprint, suitable for data centers with space and power constraints.Servers specifically designed to store and manage data as affordable entry block storages.
Support large amounts of disks like SSD and NVME Best for small and medium sized businesses