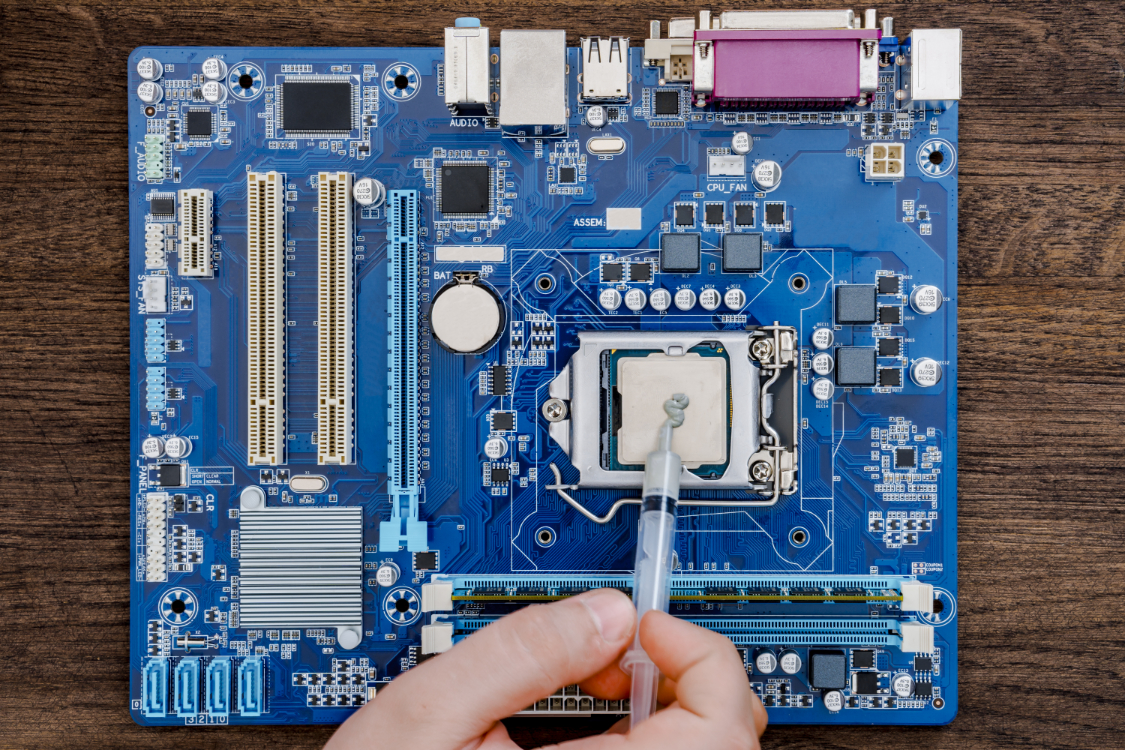
Coolers come with thermal compound pre-applied, but for PC enthusiasts who want to achieve improved temperatures at stock speeds, it’s a good idea to buy and apply new paste when installing their CPU. This is because the thermal compound that comes with the cooler is often quite old, as it’s been sitting on some shelf for months before being purchased. So while it might work to keep the temperature of their processor low, it’s not likely to produce the best results.
The thermal paste also needs changing annually. It eventually dries out and begins to lose its effectiveness. When it’s left too long, the computer starts to experience performance issues and it gradually overheats. This can cause damage to the CPU over time.
 This article explores the factors buyers need to consider when choosing the right thermal compound that will give their rig the absolute best cooling performance.
This article explores the factors buyers need to consider when choosing the right thermal compound that will give their rig the absolute best cooling performance.
What is Thermal Compound and Why is it so Important?
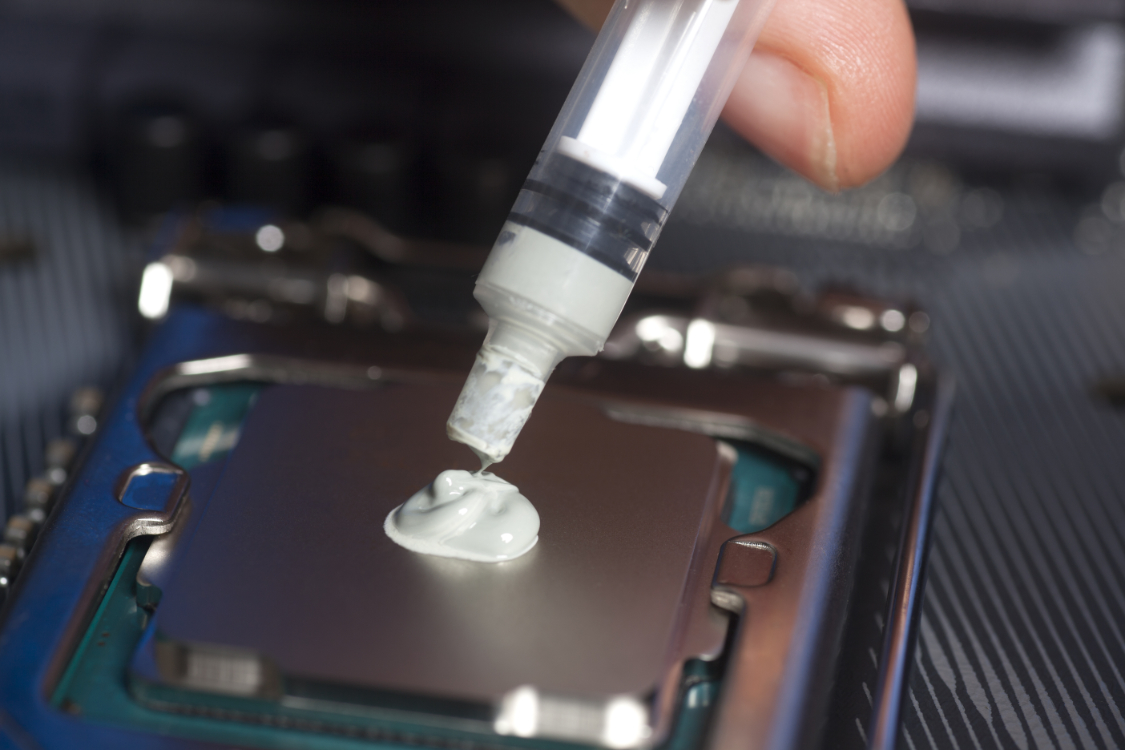

Also called thermal paste, thermal grease, or conductive grease, this compound is a heat-conductive substance that is applied between the heatsink and the device it’s meant to cool. It improves conductivity between the heatsink and the CPU. The heatsink dissipates the excess energy produced by the processor safely away from the unit, where the heat is pushed out by the fan or some other cooling apparatus.
This thermal interface material can also be applied between other components to help the system maintain a healthy temperature. This leads to a significant improvement in thermal performance and helps to prevent overheating which, in turn, increases the longevity of the CPU.
That’s why a thermal compound is important – specifically a high-quality one from outstanding brands like Artic Silver, Noctua, Cooler Master, and Thermal Grizzly.
How a Thermal Compound Works
A thermal compound works in a very simple way to help improve heat conduction. CPUs, heatsinks, and coolers have small imperfections on them that are imperceptible to the naked eye. These tiny flaws have the ability to trap air and this brings down the heatsink’s general performance. As you probably know, air is not good for heat conduction – and heatsinks are designed to conduct heat.
The thermal compound works to smooth out these microscopic spaces on and between the surfaces, making them work in the best way possible. The heatsink is then able to efficiently transfer the heat away from the component generating it.
Since the grooves between the heatsink and the processor aren’t perfectly even, the thermal compound is perfect for use as a conduit to facilitate better heat transfer. All the energy is absorbed by the CPU grease to ensure it only flows to the heatsink and not to any of the computer’s internal circuitry – something that is of particular importance for gaming PCs.
Not All Thermal Paste are the same
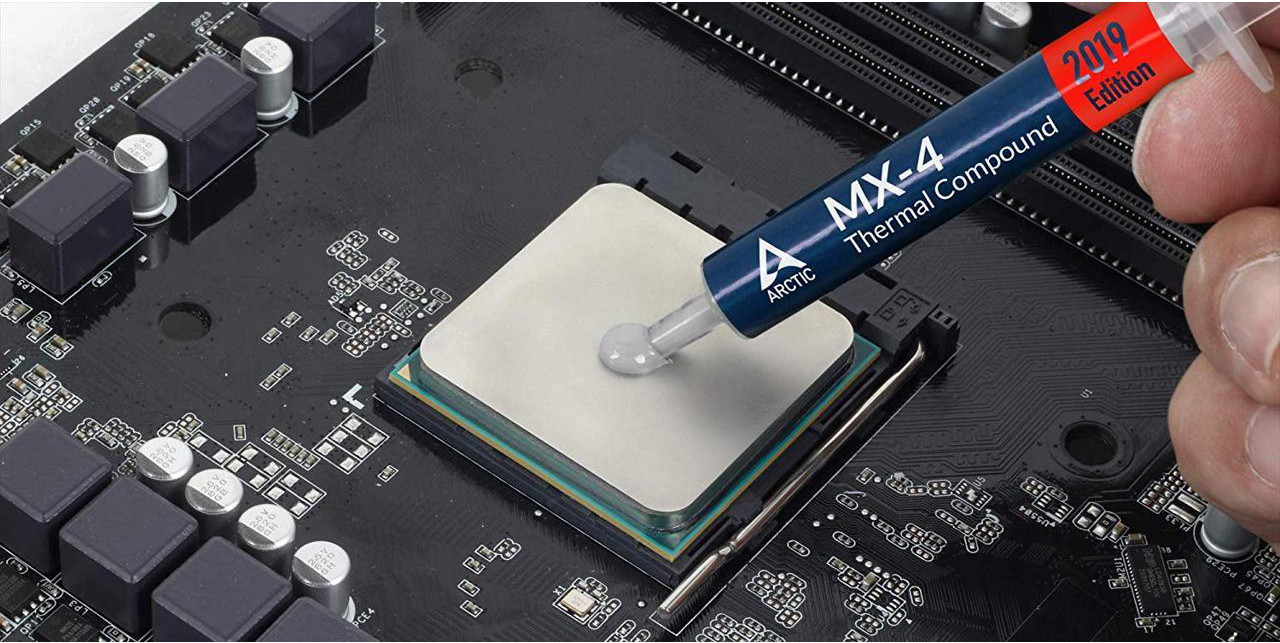

Since thermal compounds are a high-margin product, it’s no surprise that the market is so crowded. But it’s vital to note that the products aren’t all alike. The upper temperature limit of a liquid metal thermal paste can reach 150°C, although there are some pastes on the market that claim to be able to withstand temperatures of up to 300°C, and even more.
The composition of a compound determines its thermal and electrical conductivity, its durability, and its viscosity. Pastes are made of a wide range of ingredients including:
- Zinc oxide
- Silicone oil
- Ceramic
- Aluminum
- Copper
- Silver
- Graphite
- Carbon nanoparticles
- And various anti-oxidation agents
PC enthusiasts can opt for a metal, silicon, carbon-based, or ceramic thermal compound, but it’s crucial to choose one with the ideal properties to cater to their specific needs.
For instance, a gamer with a CPU that’s overclocking at breakneck speed needs to have the assurance that all the heat is being efficiently moved away from their computer’s internals, so they might choose a metal paste which has the best conduction properties.
Metal Thermal Compounds
These are the most effective heat conductors, but they are also very electrically conductive. This means that extreme care must be taken when applying the paste on the motherboard’s metal contacts.
Ceramic Thermal Compounds
These don’t contain any metal, which means that they are not conductive. These are significantly cheaper, safer to use, and they provide great results. That is why they are so popular. However, they won’t provide as large a decrease in temperature as the liquid metal thermal paste does.
Silicone Thermal Compounds
These are pre-applied to thermal pads which are then placed between the processor and the heatsink. Silicone thermal pastes are very easy to use, but they don’t offer the same effectiveness as the other types of compounds.
It’s best to avoid adhesive heat sink paste as it permanently sticks to whatever components it is used on. So, if the need ever arose to replace the cooler, for example, there would be problems in doing so.
Things to Consider When Buying Thermal Paste
Getting the wrong kind of paste will not only increase the PC temperature but it may also worsen its performance. Adequately applying the right thermal gel will keep the CPU/GPU cool without overclocking or overheating.
These are a few factors for computer enthusiasts to consider before purchasing a thermal compound that will work best to improve the temperature, as well as the performance of their PC.
Thermal Conductivity
The second factor to consider is the thermal conductivity of the paste. It’s important to choose a paste with the proper thermal conductivity levels to provide high versatility and total reliability to keep your system safe and cool. Each thermal paste comes with its own thermal conductivity rating for how efficient it is at transferring heat from the processor to the heatsink. When the thermal conductivity of a paste is more than the temperature of the components, then it’s reduced even more.
Liquid and non-metallic compounds have different conductivity levels. For the liquid thermal paste, it’s typically 70W/mK (watts per square meter of the surface area), while non-metallic compounds have a conductivity of between 4-10W/mK. As a general rule, the higher the number rating, the better the compound is going to be at heat conduction.
Density and Viscosity
In order to enhance the process of application, it’s important to choose a thermal paste that has the right density. This will allow it to squeeze throughout the CPU easily. Liquid thermal paste has a significantly lower density than normal thermal paste, but it’s also notoriously hard to apply. When choosing the right paste, care must also be taken to ensure that the paste has the right consistency for applying it directly to the CPU or GPU without risking damage to the components.
The higher the viscosity of the compound, the thicker it will be so that it looks more like an actual paste. This type of paste is typically better for sticking the heat sink compound to the processor. Compounds with lower viscosity are typically more liquid, and these tend to leak onto the motherboard easily when too much of the compound is used.
Conductive or Non-Conductive
Applying a thermal compound to the processor or other parts of the PC requires absolute care because it’s possible to experience harmful short circuits if the paste can conduct electricity. To ensure that there are no short circuits when applying the compound, it’s a good idea to choose a carbon-based compound that is free from any electrical conductivity. A compound with low conductivity can also be chosen to allow application without shorts, even if the paste touches any of the electrical components.
TDP (Thermal Design Power)
The thermal design power shows the amount of power that a processor is going to use. This can be used as an estimate to determine how hot it is going to get. A processor with higher TDP is likely to use more power and, therefore, generate a lot more heat. This is something else to consider when choosing the best thermal compound to ensure that it can handle the heat generated to keep the components safe, cool, and performing at their best. The TDP is listed on the processor specs.
Cooling Solution
Even with the best thermal compound on the market, it will be next to impossible to bring down the temperature of a system if the cooling solution being used is not a very effective one. PC users need to make sure that the cooling system they’re using is one that can adequately deal with the level of heat that their processor generates. If not, then the type of thermal compound chosen isn’t going to matter.
How Much Thermal Compound Should I Use?

Use only a pea-sized amount of paste. Apply it to the center in order to allow the heatsink to push the substance down onto the CPU. This is a great technique to prevent spreading the paste over the heat spreader and the method works particularly well with less viscous solutions. When using a liquid compound, apply a paper-thin layer over your CPU using just a dot of the substance on either side of the CPU.
What is the Shelf Life of Thermal Compounds?
Most manufacturers specify a shelf life of up to three years for packages that are unopened. However, that does not take into consideration the date the tube was produced. This means that even when enthusiasts buy compounds new, they may have been sitting on some shelf for quite a while which makes it likely that the compound has already degraded. It’s always a good idea to purchase conductive grease and other thermal compounds from larger shops with faster turnover, as a preventative measure.
Thermal Compound Products
Here is a list of suggested thermal pastes, each with it’s own pros and cons.
The Bottom Line
There’s a wide variety of thermal compounds available on the market right now. This buying guide is a great resource to use when searching for the best thermal compound to keep any system cool and enhance performance dramatically.





