When shopping for an external hard drive, there are a lot of elements to consider. You may get confused by the differences between products, or the many acronyms that stores use. That’s why we have created this external hard drive buying guide.
Internal vs. External Storage
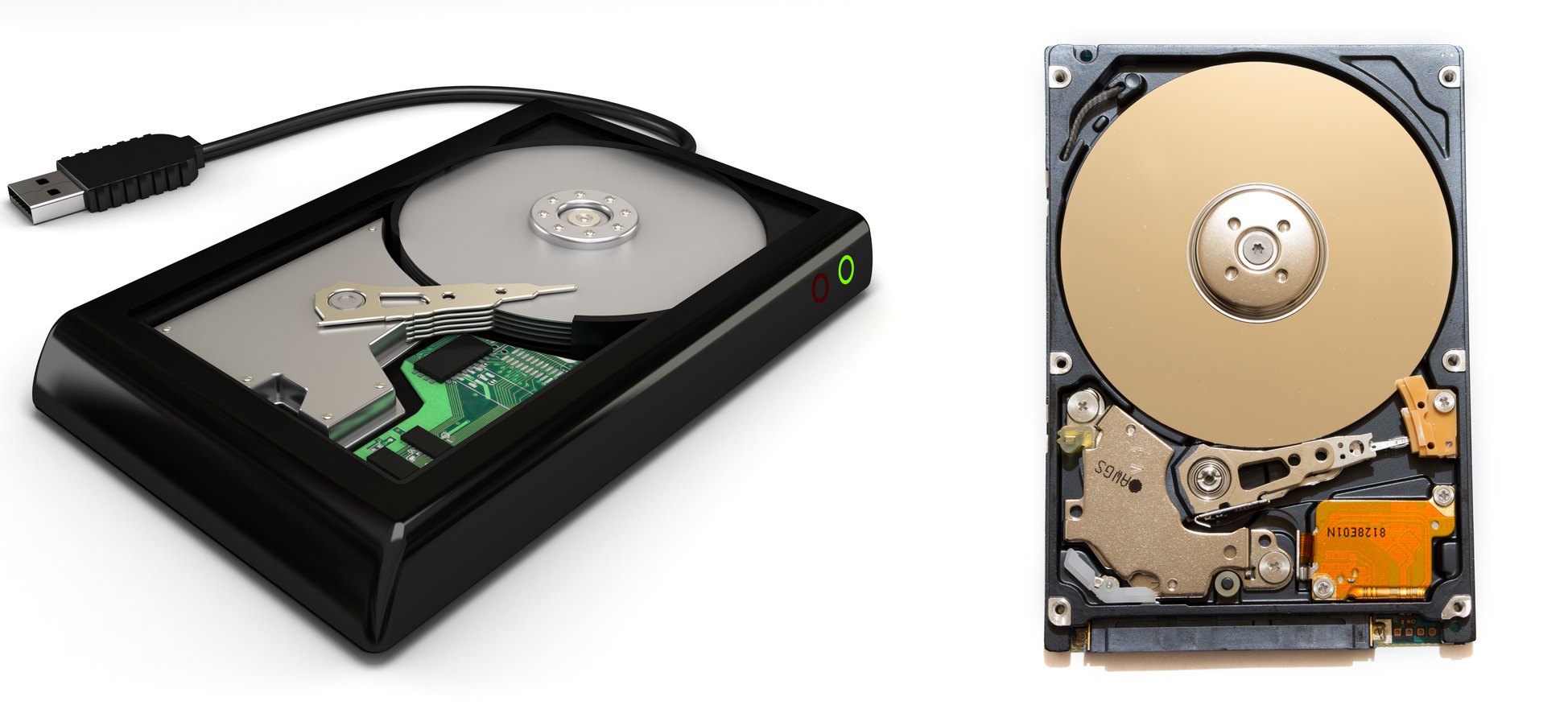
One of the major things to note about external hard drives (below left) is their difference from internal hard drives (below right). These are both storage units for a computer, but they are used in different ways. Internal hard drives are integrated in the hardware components of a computer and not something that you can easily remove from the system. These drives are also used by the system to store the key software elements of the computer like the operating system, system architecture files, installed applications, etc.
Unlike internal hard drives, external hard drives are independent and can be detachable from a computer. They are also not dedicated to any one system, but instead are independent and can be used with many different systems as long as the system can support the format of the files stored on the drive. Their hard drives are encased in a protective shell that prevents physical activity from damaging any stored information.
Probably the biggest difference between the two drive types is the cable connection they use to transfer information to and from the computer. Internal HDDs typically use a SATA connector that will plug in directly to the motherboard. External hard drives can use a number of different connections like:
- USB
- USB C (a.k.a. USB Type-C)
- eSATA
- Firewire (400 or 800)
- Thunderbolt
Each of these ports offers the user a specific read/write speed and you should consider this when you are preparing to purchase a drive. If you are looking to mitigate the time it takes for information to be added to or retrieved from the drive, you should choose a drive that offers faster read/write speeds and higher RPMs for HDDs. If you are not too concerned with fast performance, then this does not need to be as much as a factor in your decision making.
Below you can see an example of what these two devices look like. On the left is an external hard drive with a USB connector, and on the right is an internal hard drive showing all its internal components like the spindle, platters, actuator arm, etc. These are only two examples of what you might see, but they should give you a good sense of what you will be purchasing.

External Hard Drive Types
Now that you have a sense of what you are shopping for, the next big thing to consider is what external hard drive type you should buy. There are three external hard drive types that you will see, and each has its own pros and cons.

2.5 Inch External Hard Drive
2.5 inch external hard drives contain smaller disks, are lightweight, use less power/energy, and are highly portable. Their reduced size and portability provides a lot of advantages. Disadvantages include a smaller cache size, lower RPMs (sometimes), and less storage space. Usually people use these drives for portable storage, but if you are saving media files (images or videos) to storage drives like this, you may quickly run out of space. This all depends on the size of the files and the frequency that you add more information to them, but to be safe, you should probably buy something with more storage capacity.

3.5 Inch External Hard Drives
Sometimes called desktop external hard drives because of their size, these external hard drives have 3.5 inch spinning disks (a.k.a. disk platters) where data is stored. Being physically larger means the casing for these drives is considerably larger than other drive types and typically something people keep stationary next to their desktop computer as backup storage. These drives have high storage capacities and are frequently used by individuals storing hours of video production, thousands of high-resolution photos, or looking for a RAID or NAS storage solution. They are a very cost-effective solution for anyone looking to expand their computer’s storage capacity, and are easily replaced.

Solid State Hard Drive
External solid state drives (a.k.a. SSDs) are a newer technology than HDDs that store data in memory chips (solid state) instead of spinning disks that use a laser to read/write information. They are lightweight, faster than HDDs, and smaller than most HDDs. They are also less prone to physical damage if they are dropped or hit by something. All that said, SSDs at times can be more expensive than HDDs and, if you are looking to spend less money while getting as much storage capacity as you can, then this option may not be for you.
Pros & Cons of External Storage
Pros
Cons
What Can You Use an External Hard Drive For?
By this point, you probably have a good idea of what you are looking for, but you might be a little confused about why you need it or what you will use it for. External hard drives use cases are extensive, but some of the more common ones that we see are below.
Researching
When you are conducting any kind of research, you must have redundant backups that will prevent you from losing any of your data or information. If one or many of your internal hard drives die, it’s a huge relief to have copies stored on external drives. If you are a scientific researcher who has been spending years looking into something, then having all your information backed up on an external drive is almost a must.
Secure File Transfer

While arguably not the most secure way to transfer files from one computer to another, some people may not prefer cloud storage solutions or network file transfer because these are less secure storage options than saving all sensitive information to a physical, encrypted drive.
External hard drives are a good way to save all confidential information to a storage source that is 100% encrypted and can only be read by someone who has the necessary credentials. Smaller drives are also easy to transport from point A to point B, and can be very inconspicuous.
The only drawback to this is that being small means they can either be stolen or misplaced. Regardless of these minor risks, there is no doubt that using external hard drives to transfer file information from one system to the next is a secure way of keep confidential information safe – especially when compared to the alternatives.
Students / Homework

As a student, you are constantly dealing with assignments like essays, research papers, statistical analysis, etc. You have a laptop, but you need an easy way to carry assignments or important documents to places like the library or classroom computers, group project meetings, or your professor’s office. Laptops can be heavy and not always the best way to transport files from A to B. Also, they are very expensive, and there’s always the risk of them being stolen when you aren’t watching. An external hard drive is the perfect alternative that gives you the same portability as a laptop without all the same risks.
File Archive

We all have files that need to be kept safe and secure for many years. External hard drives, especially solid state drives, are an excellent way to store large amounts of information for years without needing to be concerned about losing the files or the drive. They are also a very cost effective way to digitally store information that may otherwise be kept in physical file folders in cabinets. Some of the things that you may want to have a digital copy of for years to come are:
- Tax Returns
- Important Financial Documents (EX: Bank Statements, Invoices, Receipts, etc.)
- Medical Document (EX: Birth Certificates, Release Forms, etc.)
- Applications / Employment Document
- Titles, Deeds, or Other Ownership Documents
- Academic Documents (EX: Diplomas or Degrees)
- Family Photos
- Family Videos
- Contracts
- Wills, Trusts, or Other Inheritance Documents




